13 Best Probiotics for Men – Garden of Life
Discover the benefits of probiotics for men’s digestion and immune system. Choose from a variety of supplements to support overall wellness.

In this Article:
Probiotics have become increasingly popular in recent years as a means of promoting intestinal health.
The global probiotics market has grown rapidly, with probiotics now being used not only as supplements but also in food products.
The human gut is home to trillions of bacteria, both good and bad. The good bacteria help to keep the gut healthy by preventing the growth of harmful bacteria, producing vitamins and other nutrients, and supporting the immune system.
There is some evidence that taking probiotics may be beneficial for men's health.
Research has shown that it may play a role in the development of metabolic diseases such as obesity, and diabetes, reduce the risk of urinary tract infections, and protect against prostate cancer.
This article features our picks of the 11 best probiotics for men with the brand: Garden of Life - the #1 probiotic brand in the US.
Top Probiotics for Men
Best Overall: Garden of Life Probiotics Dr. Formulated Once Daily Ultra | Skip to Review
Best Efficiency: Garden of Life Organic Probiotic Powder 5-Day Max Care | Skip to Review
Best for the Immune system: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Immune+ | Skip to Review
Best for Digestive Health: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Restore | Skip to Review
Best for Weight Loss: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Fitbiotic Weight Management | Skip to Review
Best for Prostate Health: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Prostate+ | Skip to Review
Best for Men 50+: Garden of Life Raw Probiotics for Men Over 50 | Skip to Review
Best for Colon: Garden of Life RAW Probiotics Colon Care | Skip to Review
Best for Mood: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Mood+ | Skip to Review
Best for Urinary Tract Health: Garden of Life - Acidophilus Probiotic Urinary Tract | Skip to Review
Best for Liver Health: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Liver Health+ | Skip to Review
Best for Skin: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Platinum Series Skin+ | Skip to Review
Best for Sleep: Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Restore Sleep | Skip to Review
Who Should Take Probiotics for Men?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that are believed to confer various health benefits for men when consumed in adequate amounts.
While generally considered safe for all men, the decision to take probiotics, particularly for men, should be based on specific health considerations and professional advice.
Probiotics have potential benefits for men's health in certain situations.
They may be effective in treating intestinal chronic diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)✅ and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)✅.
However, the effectiveness of probiotics in IBS treatment depends on the strains used, the different mixtures, and the dosages of these strains.
Probiotics have also shown promising results in reducing the risk of coronary artery disease and improving endothelial vascular function in men✅.
Additionally, they can have positive effects on male fertility✅ and semen quality by supporting reproductive tract eubiosis and fertility due to their antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities.
When is the best time to take probiotics for men?
The best time to take probiotics for men may depend on the type and dose of probiotics, as well as your individual health condition and preferences. However, some general guidelines are:
- Take probiotics on an empty stomach, preferably 30 minutes before a meal. This may help the probiotics survive the acidic stomach environment and reach the colon alive.
- If you take probiotics with food, choose foods that contain some fat and/or sugar, such as yogurt, kefir, oatmeal, or low-fat milk. These foods may enhance the survival of probiotics in your digestive tract.
- Take probiotics consistently, preferably at the same time every day. This may help maintain a balanced and diverse gut microbiome.
- Consult your doctor before taking probiotics, especially if you have any medical conditions or take any medications. Your doctor can help you choose the best probiotics for your needs and advise you on the optimal timing and dosage.
Probiotics can be taken at any time to promote overall gut health and improve immune function.
According to a study in 2010✅, commonly used probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains have been found to have positive effects on immune function and can help manage gastrointestinal disorders.
A 2015 meta-analysis✅ found that probiotic supplementation improved H. pylori eradication rates and reduced side effects when used with antibiotic therapy.
The optimal timing of probiotic administration is still unknown, but the study suggests that probiotics can be taken concurrently or after antibiotics.
Lv et al. also found that probiotic treatment lasting over 2 weeks and including Lactobacillus or multiple strains significantly enhanced H. pylori eradication efficacy.
Learn more:
Where Can You Buy Probiotics for Men?
Probiotics for men can be purchased from various sources.
One option is to buy probiotics from pharmacies or drugstores.
These establishments often carry a range of probiotic products specifically formulated for men's health.
Another option is to purchase probiotics online from reputable retailers or directly from manufacturers.
Many companies offer probiotic supplements that are targeted towards men's specific health needs.
You can also buy probiotics for men from various online and offline sources, depending on your preferences and budget.
Here are some possible options:
Online
You can order probiotics for men from online retailers, such as Amazon, where you can find a wide range of products, brands, prices, and reviews.
You can also buy probiotics for men from the official websites of some manufacturers, such as Garden of Life, Physic Choice, Hyperbiotics, or Ritual.
These brands have obtained USDA Organic certifications, ensuring their products are sustainably produced and safe for users.
Also, you should be careful to check the quality, safety, and authenticity of the products you buy online, and read the labels and instructions carefully before using them.
Offline
You can also buy probiotics for men from local stores, such as pharmacies, health food stores, or supermarkets, where you can see and compare the products in person.
You may also get some advice from the staff or pharmacists on how to choose the best probiotics for your needs.
However, you may have a limited selection of products and brands, and you may not be able to find the latest or most innovative probiotics for men in your area.
Why Are Probiotics for Men Different From Other Probiotics?
Probiotics for men are different from other probiotics because they may have some specific benefits for men’s health, such as supporting prostate health, testosterone levels, and weight management.
Firstly, the specific strains of probiotics used in products for men may be different.
Different strains of probiotics have different mechanisms of action and may be more effective in addressing specific health concerns.
For example, Lactobacilli strains treat urogenital infections in women✅, while certain probiotics improve intestinal barrier, oxidation, and inflammation markers in men who exercise regularly✅.
Therefore, probiotics for men may be more effective and beneficial than generic or female-oriented probiotics.
Secondly, the health concerns and conditions that probiotics for men target may be different.
Probiotics can have strain-specific and disease-specific efficacy✅.
Therefore, probiotics formulated for men may be designed to address specific male health issues, such as reproductive disorders or male fertility✅.
Additionally, cultural and socioeconomic factors may influence the consumption patterns of probiotics in men.
Some studies have found that women tend to consume more probiotics than men✅.
How Do You Choose The Best Probiotics for Men?
Choosing the best probiotics for men depends on several factors, such as your health goals, medical conditions, dietary preferences, and budget.
Firstly, it is important to select probiotics for men that have been extensively studied and have demonstrated efficacy and safety.
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB), particularly Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are among the most studied probiotics✅.
Proper administration of probiotics and prebiotics is essential, particularly when dealing with high-risk groups like infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals✅.
Additionally, probiotics for men should be able to survive through the gastrointestinal tract to exert their beneficial effects.
Probiotic strains must meet safety and functionality criteria, as well as technological usefulness, according to the selection process recommendations from WHO, FAO, and EFSA (the European Food Safety Authority)✅✅:
| Criteria | Required Properties |
|---|---|
| Safety | - Isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of healthy individuals. - History of safe use. - Precise diagnostic identification (phenotype and genotype traits). - Absence of data regarding an association with infective disease. - Absence of the ability to cleave bile acid salts. - No adverse effects. - Absence of genes responsible for antibiotic resistance localized in non-stable elements. |
| Functionality | - Competitiveness with respect to the microbiota inhabiting the intestinal ecosystem. - Ability to survive and maintain metabolic activity, and to grow in the target site. - Resistance to bile salts and enzymes. - Resistance to low pH in the stomach. - Competitiveness with respect to microbial species inhabiting the intestinal ecosystem (including closely related species). - Antagonistic activity towards pathogens (e.g., H. pylori, Salmonella sp., Listeria monocytogenes, Clostridium difficile). - Resistance to bacteriocins and acids produced by the endogenic intestinal microbiota. - Adherence and ability to colonize specific sites within the host organism, and an appropriate survival rate in the gastrointestinal system. |
| Technological usability | - Easy production of high biomass amounts and high productivity of cultures. - Viability and stability of desired properties of probiotic bacteria during the fixing process (freezing, freeze-drying), preparation, and distribution of probiotic products. - High storage survival rate in finished products (in aerobic and micro-aerophilic conditions). - Guarantee of desired sensory properties of finished products (in the case of the food industry). - Genetic stability. - Resistance to bacteriophages. |
The selection of probiotics can also depend on the specific health condition or target pathogen✅.
For example, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus is a well-studied probiotic that has been identified as a potential candidate for the development of new bioengineered probiotic strains aimed at controlling specific pathogens.
Men can benefit from taking probiotics that are tailored to address specific health conditions:
| Probiotic Strain | Specific Health Conditions |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | Diarrhea, constipation, allergies |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum | Diarrhea, constipation |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Diarrhea, allergies |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | Diarrhea |
| Enterococcus faecium PTA 5844 | Gastrointestinal infections |
| Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 | Gastrointestinal infections |
Here are some guidelines based on expert consensus to help you choose the best probiotics for men:
- Look for specific strains: Different probiotic strains have different effects on health. It is important to choose a probiotic that contains strains that have been studied and shown to have benefits for men's health. For example, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG has been shown to enhance immune response, while Lactobacillus reuteri may have benefits for prostate health.
- Consider the CFU count: CFU stands for colony-forming units, which indicates the number of viable bacteria in a probiotic supplement. Higher CFU counts may be more effective, but it is important to note that the optimal dosage can vary depending on the strain and the specific health condition being targeted.
- Check for viability and stability: Probiotics are live bacteria, so it is important to choose a product that ensures the viability and stability of the strains. Look for products that have been tested for shelf stability and have appropriate packaging to protect the bacteria from moisture and heat.
- Assess the quality and safety: Choose probiotics from reputable manufacturers that follow good manufacturing practices (GMP) and have undergone third-party testing for quality and safety. Look for products that are free from contaminants and have clear labeling of the strains and CFU counts.
- Consider your specific health needs: Different probiotics may have specific benefits for certain health conditions. Consider your individual health needs and choose a probiotic that aligns with those needs. For example, if you are looking to support digestive health, a probiotic with strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus may be beneficial.
Benefits of Probiotics For Men
Probiotics have been extensively researched for their potential health benefits, and men stand to gain a lot from incorporating them into their daily routines.
From weight management to immunity, prostate health to mood regulation, the advantages are numerous.
Additionally, probiotics can improve reproductive and sexual health, colon health, urinary tract health, liver health, skin health, and even sleep quality.
So why not consider adding them to your diet today?
- Weight loss: Probiotics may aid weight loss by affecting gut bacteria balance, which can impact fat storage, blood sugar regulation, and hormone response to hunger and fullness. Studies suggest that probiotics could reduce body weight, BMI, and fat percentage in overweight or obese people, although effectiveness may depend on the type, dosage, and duration of treatment✅.
- Immunity health: Probiotics enhance the immune system by increasing natural antibodies and stimulating immune cells. They may also prevent or treat infections, including respiratory and urinary tract infections, as well as Helicobacter pylori infections that can lead to stomach ulcers and cancer✅.
- Prostate health: Probiotics can promote prostate health by reducing inflammation and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria that can cause prostatitis. Additionally, they may lower the risk of prostate cancer by inhibiting the production of carcinogenic compounds and inducing programmed cell death in cancer cells✅.
- Reproductive or sex health: Probiotics may improve sperm quality and motility, potentially benefiting fertility and sexual performance. They may also help prevent or treat sexually transmitted infections by inhibiting the adhesion and invasion of pathogens to the genital mucosa✅.
- Colon health: Probiotics can improve gut health, preventing or alleviating conditions such as IBS, IBD, constipation, diarrhea, and colorectal cancer. They also enhance the intestinal barrier, reducing the risk of inflammation by preventing the entry of toxins and pathogens into the bloodstream✅.
- Mood health: Probiotics may improve mood by influencing the gut-brain axis and modulating the production and function of neurotransmitters. They may also reduce stress, anxiety, and depression by lowering cortisol levels and enhancing coping skills✅.
- Urinary tract health: Probiotics may help prevent or treat UTIs by competing with harmful bacteria, producing antimicrobial substances, and modulating immune responses. This is especially relevant for women who are more prone to UTIs, but men can also be affected✅.
- Liver health: Probiotics may benefit liver health by reducing inflammation and fibrosis, which are associated with chronic liver diseases like alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis. They may also lower the levels of liver enzymes such as ALT and AST, which are markers of liver damage✅.
- Skin health: Probiotics can improve skin health by enhancing skin barrier function, hydration, elasticity, and appearance. They can also prevent or treat skin conditions such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, and atopic dermatitis by regulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and microbial balance. Studies have supported these claims✅.
- Sleep health: Probiotics may improve sleep health by regulating circadian rhythms and impacting melatonin production. They can also reduce stress and anxiety levels, leading to better sleep quality✅.
| Probiotic Strains | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus gasseri | Reduce body weight and waist circumference in overweight individuals✅. |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | Enhance immune response and reduce the risk of respiratory tract infections✅. |
| Bifidobacterium longum | May help improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression ✅. |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | Help improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria ✅. |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | May help improve symptoms of acne and other skin conditions ✅). |
| Lactobacillus reuteri | Reduce inflammation and promote a healthy balance of bacteria in the urogenital tract ✅. |
Our Pick of Best Probiotics for Men - Garden Of Life
Garden of Life Probiotics Dr. Formulated Once Daily Ultra
Garden of Life Probiotics Dr. Formulated Once Daily Ultra
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (1,082 ratings)
- 600+ bought in past month
- -12%$35.00 ($1.17/Count)

Product Description
- Dr. David Perlmutter's Once Daily Ultra is a probiotic supplement that supports digestive, colon, and immune system health.
- The formula contains 90 billion CFU from 15 diverse and hardy probiotic strains, including L. acidophilus NCFM® and Lactobacillus plantarum, L. rhamnosus, L. acidophilus, Bifidobacterium lactis, B. bifidum, and B. longum.
- The probiotic strains in this formula can survive in the gut, making them effective in supporting gut health.
- The formula also includes prebiotics to feed good bacteria in the gut, with an Organic Prebiotic Fiber blend containing Organic Potato and Organic Acacia (A. senegal) to help beneficial bacteria thrive.
- Dr. Formulated Once Daily is Third-Party Certified Non-GMO Project Verified and NSF Gluten-Free, as well as Vegetarian and Hypoallergenic (Dairy Free, Gluten-Free, Soy-Free, and Wheat-Free).
- The creator of this formula is Dr. David Perlmutter, a Board-Certified Neurologist, #1 New York Times best-selling author, Fellow of the American College of Nutrition, and expert in the human microbiome.
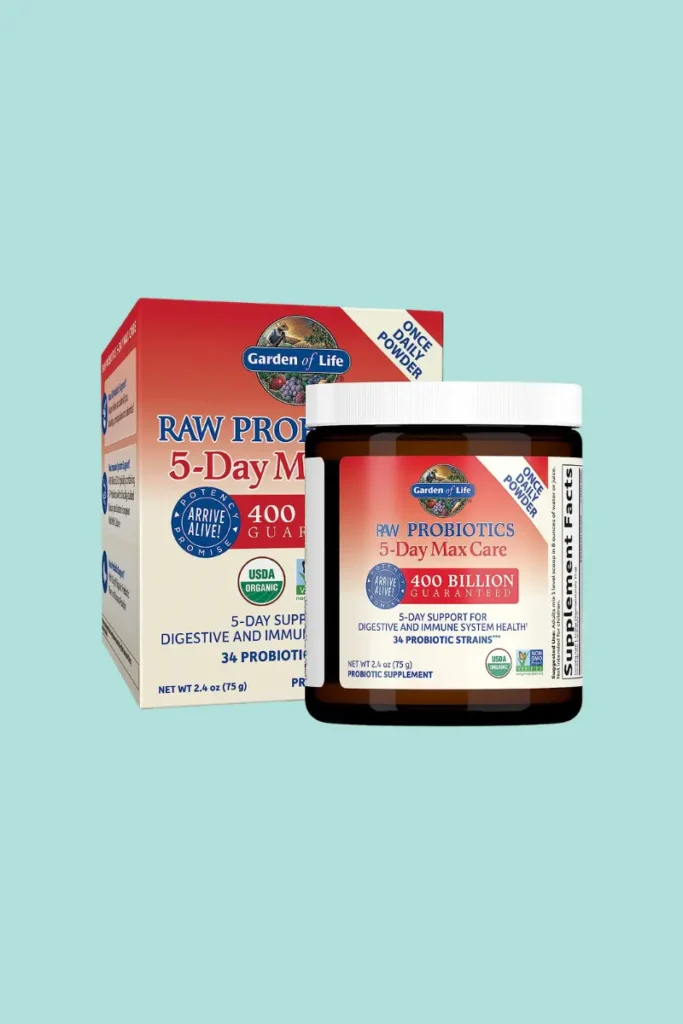
Garden of Life Organic Probiotic Powder 5-Day Max Care
Garden of Life Organic Probiotic Powder 5-Day Max Care
- 4.5 out of 5 stars (666 ratings)
- 100+ bought in past month
- -20% $33.59 ($14.00 / Ounce)
Product Description
- Many factors can compromise your body’s defenses, including the overuse of medications, stress, your environment, cleansing, and even normal aging, resulting in the loss of beneficial Bifidobacterium.
- Raw Probiotics 5-Day Max Care for Adults is your ultimate, complementary probiotic powder to achieve balance and help you repopulate your gastrointestinal tract with good bacteria.
- This unique High Bifido formula provides MAX GI probiotic support, with 400 Billion CFU Guaranteed from 34 probiotics including Clinically Studied species plus Eastern European Wild Kefir Culture, to help relieve occasional gas, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
- This powdered probiotic also has a Full Spectrum Enzyme Blend of Digestive Enzymes including DPP IV Protease, plus a Replenish Prebiotic Fiber Blend with Organic Jerusalem Artichoke Inulin and Organic Banana Powder.
- Simply mix up to 1 1/2 Tablespoons of powder in water or juice once daily over a 5-day period.- Probiotic potency is guaranteed through expiration.
- We begin with high levels of probiotics to ensure viability, even if the product is warm for a few days during shipment (especially during summer or in warmer climates); simply refrigerate upon receipt.
- 5-Day Max Care is Third-Party Certified USDA Organic, Non-GMO Project Verified, and NSF Certified Gluten-Free.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Immune+
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Immune+
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (1,351 ratings)
- 500+ bought in past month
- $56.99 ($1.90$1.90 / Count)

Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter formulated a new "Platinum" Series with cutting-edge probiotic strains, clinically researched ingredients, and high-CFU counts.
- The Platinum series meets a growing demand for therapeutic, effective, and unique nutritional products, personalized to individual health concerns.
- Over 70% of our immune system resides in our digestive tract.
- Immune+ probiotic is a targeted formula, including two of the most widely studied probiotics L.Acidophilus NCFM and L. Rhamnosus GG.
- The diverse strains in Immune+ probiotics are resistant to stomach acid and bile.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Restore
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Restore
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (1,351 ratings)
- 1K+ bought in past month
- $41.29 ($1.47 / Count)

Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter developed the "Platinum" Series with advanced probiotic strains, clinically researched ingredients, and high-cfu counts, based on the latest science in human microbiome.
- The Platinum series caters to the increasing demand for personalized, effective, and unique nutritional products that target individual health concerns.
- During and after times of digestive compromise, the digestive system requires extra care. Restore probiotic is a potent formula with 200 billion CFU of beneficial probiotics, made from diverse strains that are resistant to stomach acid and bile, providing additional digestive and immune system support.
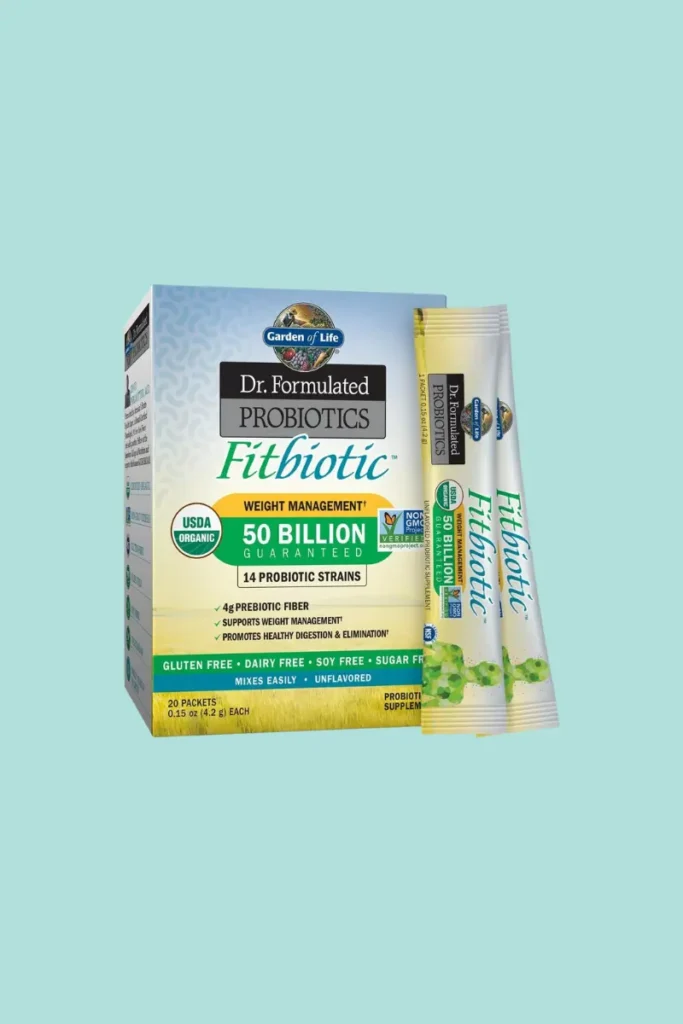
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Fitbiotic Weight Management
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Fitbiotic Weight Management
- 4.4 out of 5 stars (1,009 ratings)
- 700+ bought in past month
- $30.34 ($10.11 / Ounce)
Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter has developed a new approach to weight loss support that complements your current diet and exercise program.
- Fitbiotic is a unique, raw probiotic formula that is Certified USDA Organic.
- This formula contains 4g of prebiotic fiber from premium Organic Acacia (A. Senegal), 14 probiotic strains, and 50 billion CFU.
- Fitbiotics are an ideal choice for those looking to manage their weight.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Prostate+
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Prostate+
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (1,961 ratings)
- Capsule
- $48.15 ($0.80 / Count)
Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter formulated a unique supplement to support lower urinary tract and prostate health in aging men.- Prostate+ contains clinically studied organic whole cranberry fruit, probiotics, and vitamin D3.
- The supplement has 500mg of Organic Flowens, the clinically studied amount in "Gold Standard" human trials for prostate health and normal urine flow.
- Flowens is a certified organic cranberry powder designed to support men’s prostate health.
- Clinically studied Flowens has a published safety study and contains no sugar, calories, carriers, additives, or preservatives.
- Prostate+ also contains 50 billion CFU from 15 probiotics, including B. animalis subsp. lactis for digestive and immune system support as well as 1,000 IU of whole food vitamin D3 for prostate health.
Garden of Life Raw Probiotics for Men Over 50
Garden of Life Raw Probiotics for Men Over 50
- 4.7 out of 5 stars (916 ratings)
- 500+ bought in past month
- $40.90 ($0.45 / Count)

Product Description
- Maintaining a balanced bacterial environment in your digestive system is essential for overall well-being.
- Garden of Life Raw Probiotics Men 50 & Wiser is a high-potency, whole-food probiotic formula that contains probiotic strains clinically proven to support colon health, bowel regularity, and overall digestive function.
- This probiotic for men over 50 contains 32 original probiotics, including L. fermentum and B. animalis sub. Lactis, which are specifically formulated for men in their 50s and beyond. It supports colon health, gut-related immunity, and prostate health.
- Men 50 & Wiser Raw Probiotic also delivers probiotic-created vitamins, minerals, and prebiotics, as well as dairy-digesting enzymes to help break down lactose and casein.
- This probiotic goes beyond probiotics and offers a wide range of benefits specifically targeted for men over 50. It is RAW, which means it is uncooked, untreated, unadulterated, with no binders or fillers, and no carriers such as maltodextrin or dextrose.
- Probiotic potency is guaranteed through expiration, and it is third-party tested and certified non-GMO by the Non-GMO Project and certified gluten-free by NSF.
- Simply refrigerate upon receipt, even if the product is warm for a few days during shipment (especially during summer or in warmer climates).
Garden of Life RAW Probiotics Colon Care
Garden of Life RAW Probiotics Colon Care
- 4.5 out of 5 stars (2,584 ratings)
- 4K+ bought in past month
- $29.39 ($0.98 / Count)
Product Description
- Garden of Life RAW Probiotics Colon Care supports regular, healthy, and comfortable movements by maintaining a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the colon.
- Each high-potency RAW Probiotics formula contains over 30 beneficial probiotics strains from Bulgarian yogurt and Eastern European wild kefir, guaranteed to Arrive Alive!
- RAW Probiotics Colon Care is a high-potency, RAW, whole food probiotic formula featuring probiotic strains clinically studied to promote healthy, comfortable colon transit time, elimination, and to support the immune system.
- The proprietary Colon Care Blend in RAW Probiotics Colon Care contains 50 billion live probiotic cultures in a convenient once-daily capsule.
- When you need colon probiotic support, turn to Garden of Life RAW Probiotics Colon Care and empower your extraordinary health.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Mood+
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Mood+
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (6,747 ratings)
- 10K+ bought in past month
- $31.12 ($0.52 / Count)

Product Description
- Dr. Formulated Probiotics Mood is a unique probiotic formula designed to support mood and relaxation.
- It contains clinically studied strains, including L. helveticus R0052 and B. longum R0175, which have been shown to support mood and relaxation.
- This formula also includes 350mg of organic ashwagandha and organic Alaskan blueberries, both of which are known for their mood-boosting properties.
- With just 2 capsules a day, you can support your gut and brain health.
Garden of Life – Acidophilus Probiotic Urinary Tract
Garden of Life – Acidophilus Probiotic Urinary Tract
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (3,345 ratings)
- 5K+ bought in past month
- $34.38 ($0.57 / Count)

Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter formulated a unique blend of probiotics, clinically studied organic whole cranberry, and vitamin D3 to support healthy urinary tract function and promote the growth of good bacteria in women and men.
- Urinary Tract contains 500mg of organic Pacran cranberry, which is the clinically studied amount in Gold Standard human trials.
- Pacran is a certified organic cranberry powder that is specifically designed to support urinary tract health.
- The Urinary Tract also contains 50 billion CFU from 16 probiotics, including L. reuteri and L. acidophilus NCFM, as well as whole food vitamin D (1,000IU) nutrient support for immune system health.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Liver Health+
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Platinum Series Liver Health+
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (172 ratings)
- 300+ bought in past month
- $34.23 ($1.14 / Count)
Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter created the Platinum Series with advanced probiotic strains, clinically researched ingredients, and high-cfu counts, based on emerging science in the human microbiome.
- The Platinum Series caters to the growing demand for personalized and effective nutritional products that address individual health concerns.
- A healthy microbiome is crucial for supporting all organs involved in detoxification and elimination, especially the liver.
- The Liver Health+ Probiotic is a targeted formula made from diverse strains that are resistant to stomach acid and bile, providing daily support for detoxification, digestion, and the immune system.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Platinum Series Skin+
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Platinum Series Skin+
- 4.6 out of 5 stars (179 ratings)
- 200+ bought in past month
- $38.95 ($1.30 / Count)

Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter created the Platinum Series with cutting-edge probiotic strains, clinically researched ingredients, and high-CFU counts, based on emerging science in the human microbiome field.
- The Platinum series offers therapeutic, effective, and personalized nutritional products to address individual health concerns.
- Skin health is closely related to the health of the microbiome, which is the body's largest organ.
- Skin+ probiotic is a targeted formula made from diverse strains that are resistant to stomach acid and bile.
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Restore Sleep
Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Restore Sleep
- 4.2 out of 5 stars (63 ratings)
- 100+ bought in past month
- -45% $33.00 ($1.18 / Count)

Product Description
- Dr. Perlmutter's Restore Sleep Probiotic with Herbs is a highly potent formula that contains 200 billion CFU of beneficial probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics.
- It includes 11 probiotic strains for digestive and immune support such as Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Bacillus subtilis.
- The formula also has a 450mg Organic Sleep Blend containing Organic Lemon Balm, Valerian Root, Chamomile, and Passionflower to promote restful sleep.
- Emerging science suggests that postbiotics, the metabolites of probiotics, play an essential role in gut health.
- The 125 mg Pre- & Post-biotic Blend provides probiotic fiber from Organic Acacia (A. senegal) and Organic Potato, as well as Clinically Studied postbiotic Immuno-LP20™ (tyndallized Lactobacillus plantarum L-137).
- The Physician behind our Doctor Formulated line is David Perlmutter, M.D., America's Brain-Health Expert, a Board-Certified Neurologist, #1 New York Times best-selling author, Fellow of the American College of Nutrition, and expert in the human MICROBIOME.
- Restore Sleep Probiotic with Herbs helps to replenish the gut with good bacteria overnight and promotes a full night of deep rest with only 2 capsules a day.
Frequently Asked Question
Here are some FAQs sections about men's probiotics:
What does a probiotic do for men?
Probiotics have potential benefits for men's health, including reducing the risk of upper respiratory tract infections and improving muscle recovery after exercise. Specific probiotic strains have been shown to be effective in reducing the severity and duration of URTIs in athletes. However, more research is needed to determine the optimal dosages and specific effects of probiotics for men, and it is important to note that there may be differences in the effects of probiotics between men and women. The gut microbiota composition of athletes, including men, may differ from that of sedentary individuals, which suggests that athletes may have unique gut microbiota profiles that could potentially benefit from probiotic supplementation.
What's a good probiotic for a man?
When selecting the right probiotic for men's health, we need to consider factors such as specific strains, scientific studies, healthcare professional guidance, and labeling information:
- Strain Selection: It's crucial to choose probiotic strains that have been specifically studied and shown to benefit men's health. Studies like Lamprecht et al. (2012) and Jäger et al. (2019) demonstrate the positive effects of probiotics on markers of intestinal health, inflammation, and recovery in trained men and athletes, respectively.
- Healthcare Professional Guidance: Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable when selecting a probiotic. Fijan et al. (2019) found that most health professionals have at least a medium level of knowledge about probiotics, making them valuable sources of guidance in choosing the right probiotic.
- Strain Identification and Potency: The International Society of Sports Nutrition recommends that probiotic products should clearly label the genus, species, and strain of each live microorganism, along with the total estimated quantity of each probiotic strain at the end of the product's shelf life. This information is essential for ensuring the quality and effectiveness of the probiotic product.
How often should men take probiotics?
The frequency of probiotic intake for men is not explicitly mentioned. There are some insights into the potential benefits of probiotics for men's health:
Lee et al. (2017) conducted a study on rats and found that Lactobacillus farciminis probiotics reduced colonic microinflammation, suggesting potential benefits for reducing inflammation in the colon relevant to men's health.
Myles et al. (2020) conducted a study on rats and observed sex-dependent effects of probiotics on physiological and behavioral outcomes in response to a Western diet. In males, the probiotic appeared to mitigate the effects of the diet on weight gain and calorie intake, highlighting potential gender-specific responses to probiotics.
Individual responses to probiotics can vary, and it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on probiotic use for men's health.
Can men take probiotics daily?
Probiotics are live microorganisms found in fermented foods and dietary supplements that offer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts.
Limited research exists specifically addressing whether men can take probiotics daily, but they are generally safe for men with few side effects.
Probiotics have demonstrated positive effects on gut health, immune function, and overall well-being.
Probiotics have been studied in the context of cardiovascular health, where they can reduce blood lipids and improve endothelial vascular function in patients with coronary artery disease.
Probiotics may also have potential benefits for bone health, particularly in postmenopausal women, although the effects on bone mineral density are not yet conclusive.
The effects of probiotics can vary based on specific strains, dosages, and individual factors like age, sex, and overall health.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, including probiotics, due to individual variability and potential interactions.
References
Fitnature uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Opinion of the Scientific Committee on a request from EFSA related to a generic approach to the safety assessment by EFSA of microorganisms used in food/feed and the production of food/feed additives. EFSA J. 2005, 226, 1–12
- Akbarzadeh, Fariborz, et al. “Dairy Probiotic Foods and Coronary Heart Disease: A Review on Mechanism of Action.” IntechOpen, 3 Oct. 2012, https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/39617. Accessed 26 Aug. 2023.
- Authority, European Food Safety. “Opinion of the Scientific Committee on a Request from EFSA Related to A Harmonised Approach for Risk Assessment of Substances Which Are Both Genotoxic and Carcinogenic.” European Food Safety Authority, 27 Oct. 2005, https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/282. Accessed 28 Aug. 2023.
- Hashem, Nesrein M., and Antonio Gonzalez-Bulnes. “The Use of Probiotics for Management and Improvement of Reproductive Eubiosis and Function.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 4, Feb. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040902.
- Kechagia, Maria, et al. “Health Benefits of Probiotics: A Review.” International Scholarly Research Notices, vol. 2013, Jan. 2013, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5402/2013/481651.
- Kim, Young Sun, and Nayoung Kim. “Sex-Gender Differences in Irritable Bowel Syndrome.” Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, vol. 24, no. 4, Oct. 2018, pp. 544–58, https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm18082.
- Lamprecht, Manfred, et al. “Probiotic Supplementation Affects Markers of Intestinal Barrier, Oxidation, and Inflammation in Trained Men; a Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, vol. 9, no. 1, Feb. 2012, https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-9-45.
- Landström, Eva, et al. “Use of Functional Foods among Swedish Consumers Is Related to Health-Consciousness and Perceived Effect.” British Journal of Nutrition, vol. 98, no. 5, pp. 1058–69, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114507761780. Accessed 26 Aug. 2023.
- Lv, Zhifa, et al. “Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics as Adjuvant Agents for Helicobacter Pylori Infection: A Meta‑analysis.” Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 707–16, https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2174. Accessed 26 Aug. 2023.
- Mathipa-Mdakane, Moloko G., and Mapitsi S. Thantsha. “Lacticaseibacillus Rhamnosus: A Suitable Candidate for the Construction of Novel Bioengineered Probiotic Strains for Targeted Pathogen Control.” Foods, vol. 11, no. 6, Mar. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11060785.
- McFarland, et al. “Strain-Specificity and Disease-Specificity of Probiotic Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Frontiers in Medicine, vol. 5, May 2018, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00124.
- O’Connor, A., et al. “The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Gut Microbiota Composition, Immunological and Biochemical Markers in Healthy Volunteers.” Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, vol. 69, no. OCE1, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665109992746. Accessed 26 Aug. 2023.
- Ooi, Lay-Gaik, and Min-Tze Liong. “Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Probiotics and Prebiotics: A Review of in Vivo and in Vitro Findings.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 11, no. 6, June 2010, pp. 2499–522, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11062499.
- Plaza-Díaz, Julio, et al. “Evidence of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Intestinal Chronic Diseases.” Nutrients, vol. 9, no. 6, May 2017, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9060555.
- van den Nieuwboer, M., et al. “Safety of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Children under 18 Years of Age.” Beneficial Microbes, vol. 6, no. 5, Oct. 2015, pp. 615–30, https://doi.org/10.3920/bm2014.0157.
- Zmora, Niv, et al. “Personalized Gut Mucosal Colonization Resistance to Empiric Probiotics Is Associated with Unique Host and Microbiome Features.” Cell, vol. 174, no. 6, Sept. 2018, pp. 1388-1405.e21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.041.
Review date not set.
How we reviewed this article:
Latest on: